Ceramic Density Formula
Here follows a basic summary of the procedure.
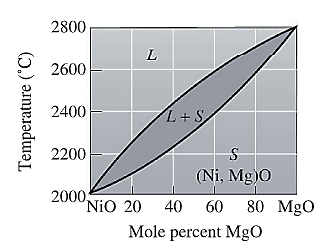
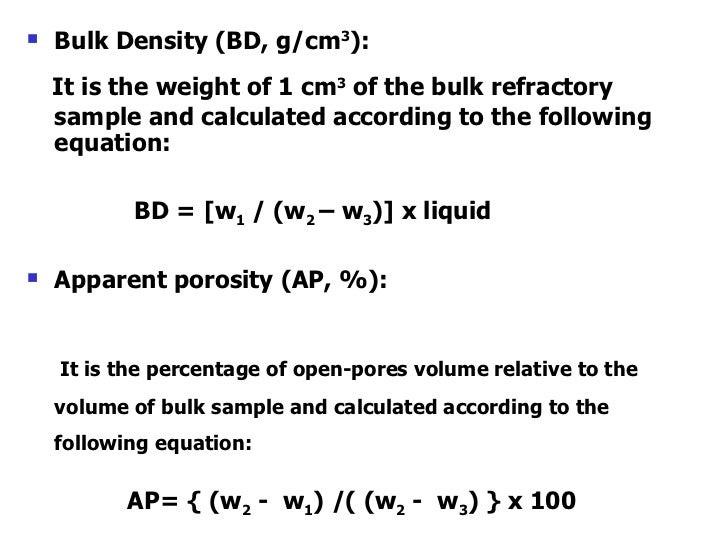
Ceramic density formula. Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications. A formal procedure is described in astm c373 not publicly available unfortunately and it needs only water and a weight scale. Some ambiguity may result when the experimental density of a ceramic porous body is simply referred to because several experimental densities can be actually defined depending on how volume. We have collected a number of charts detailing applications and properties for some of the most commonly used ceramic materials.
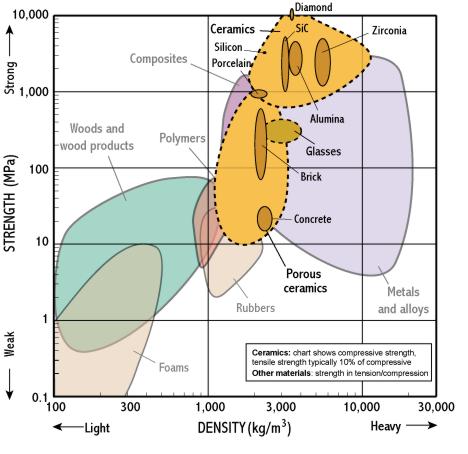
A ceramic material is an inorganic non metallic often crystalline oxide nitride or carbide material. While the data in these charts is in most cases typical of what you will find from ceramic component suppliers it is only intended to be a general point of reference and should not be used for material selection or specification. Ceramics are intermediate in density between polymers lower and metals higher in the range of 2 6 gms cm3. Due to the difficulty of measuring ceramic tile porosity bulk density is the physical magnitude that is actually measured to control the pressing stage.
Some elements such as carbon or silicon may be considered ceramics ceramic materials are brittle hard strong in compression and weak in shearing and tension. Compositions with several allotropes such as sio2 will have minor differences in density. The density and porosity of a ceramic body can be obtained through archimedes principle. Non crystalline materials are less dense than crystalline ones.
Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids. By measuring the density of the product it becomes easier to regulate porosity and adjust formulations accordingly. They withstand chemical erosion that occurs in other materials subjected to acidic or caustic environments.
It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic. Measuring the density of a ceramic body.










.jpg)
.jpg)