Ceramic Fiber Heat Transfer Coefficient
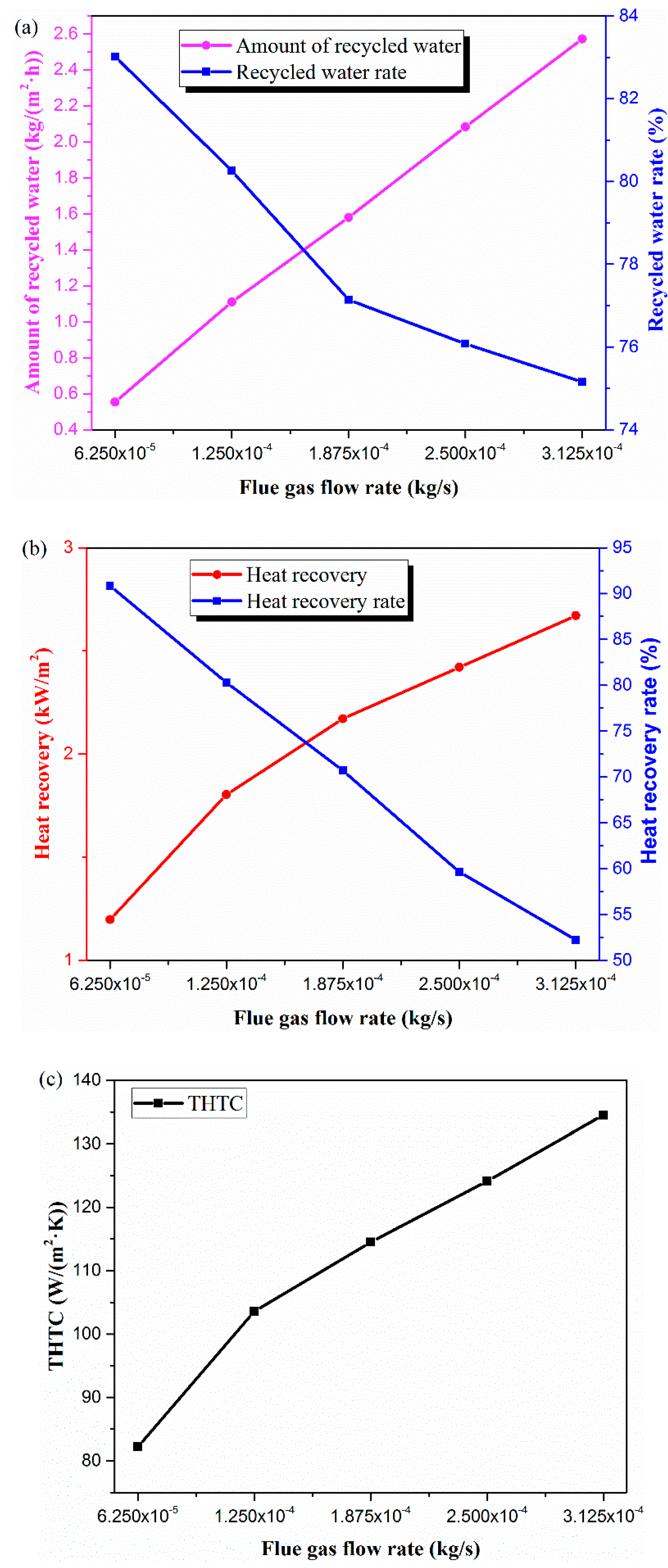
Conductive heat transfer per unit area can be.
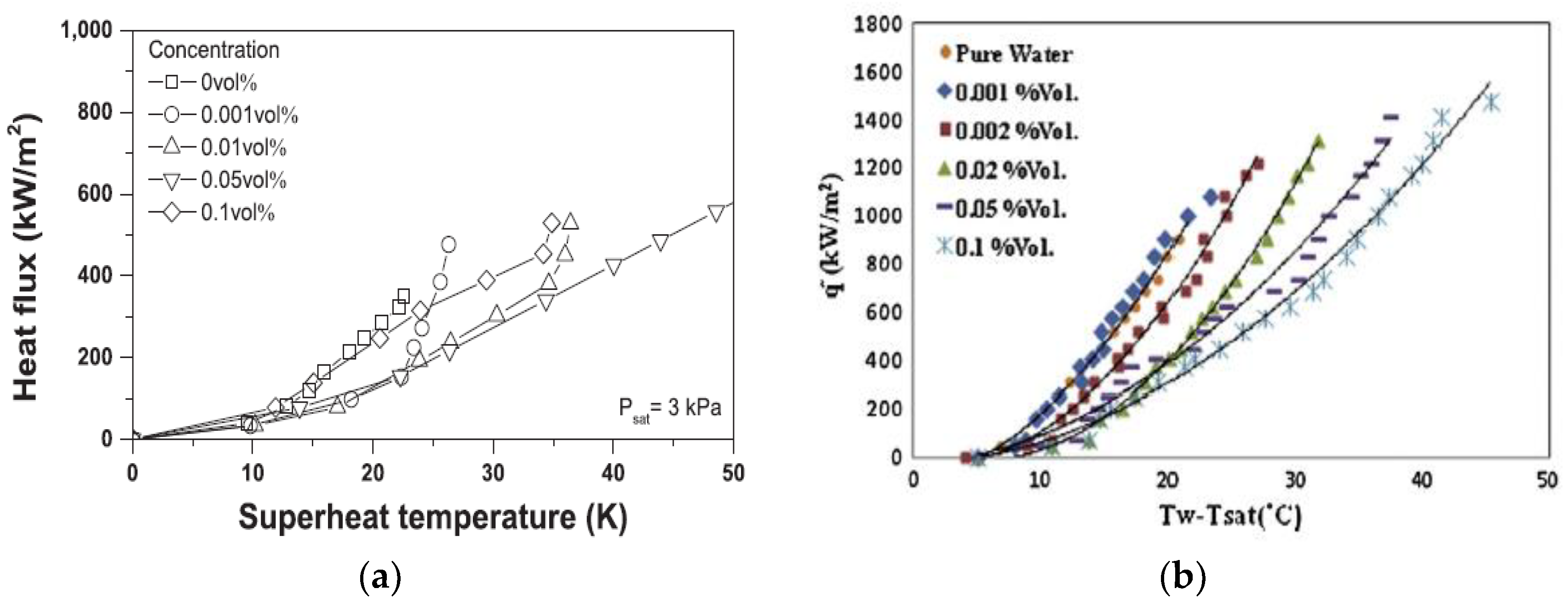
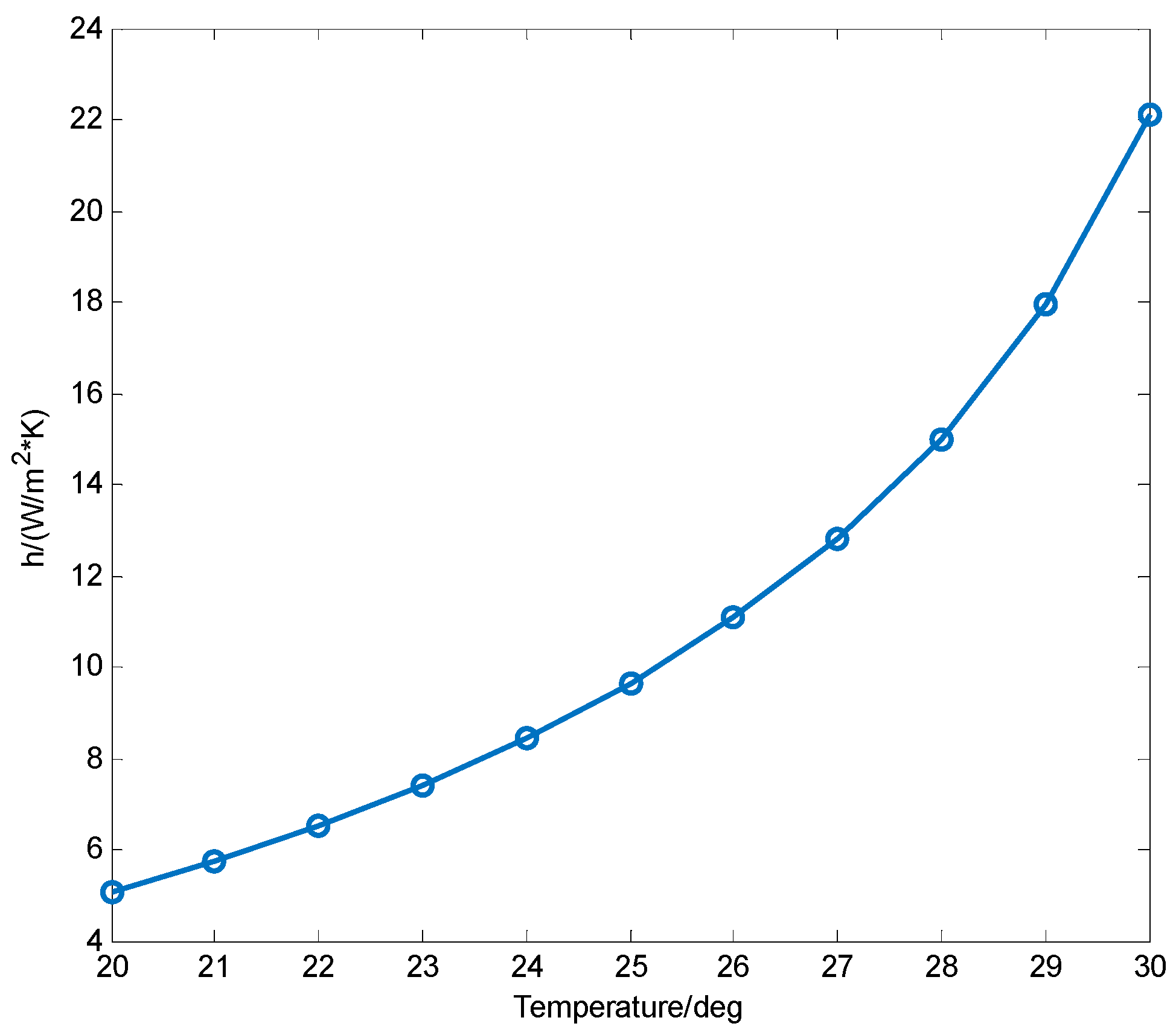
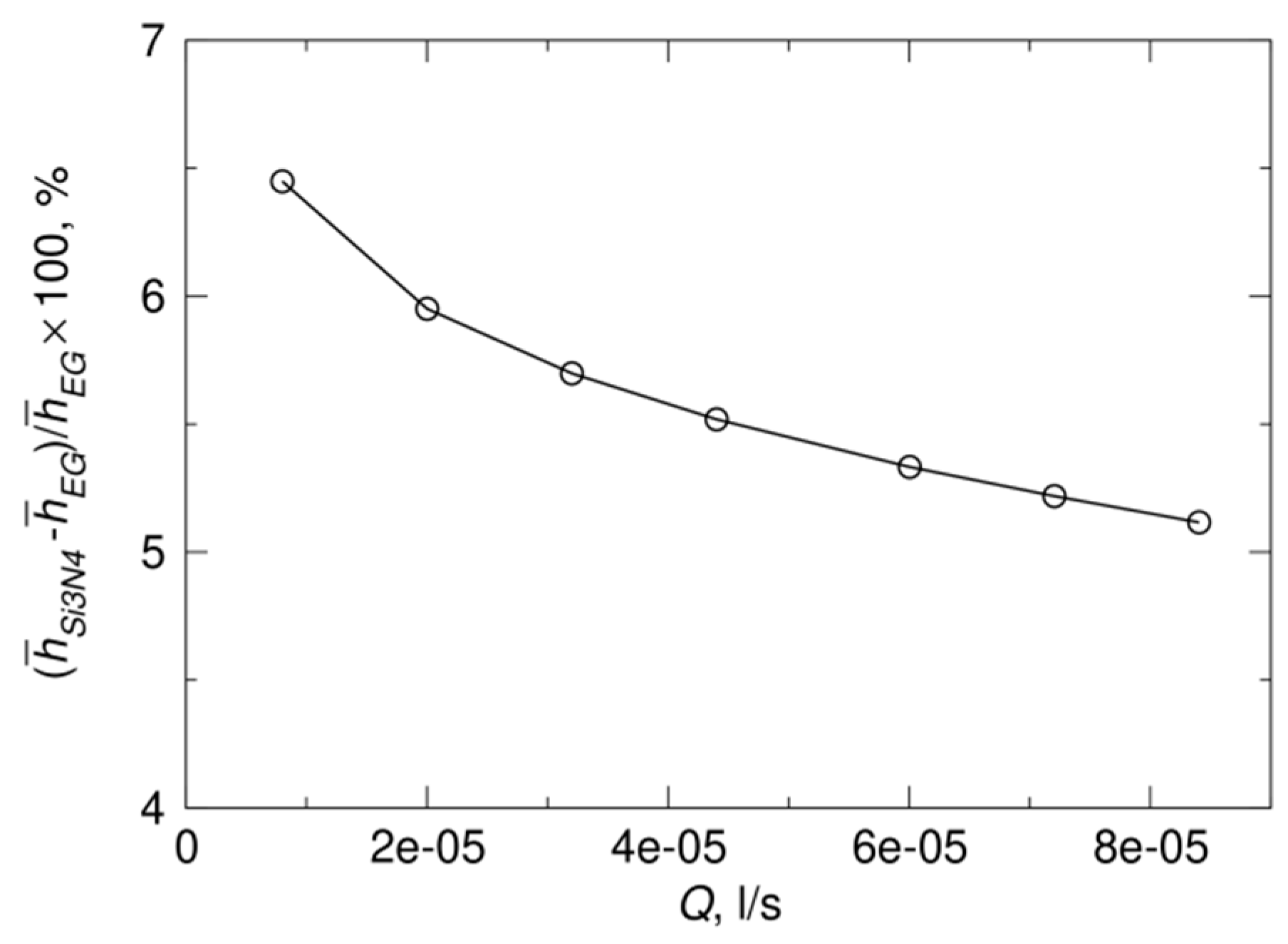
Ceramic fiber heat transfer coefficient. The thermal conductivities of ceramic based substrates are usually one or two orders of magnitude higher than those of conventional epoxy based substrates. Heat transfer by convection is emphasized by the present treatment. The advanced ceramic fiber materials are potential candi and conductivity at high temperature. Heat transfer coefficients resulted within 40 500 w m 2 k 1 varying the superficial air velocity from 0 5 to 5 m s 1.
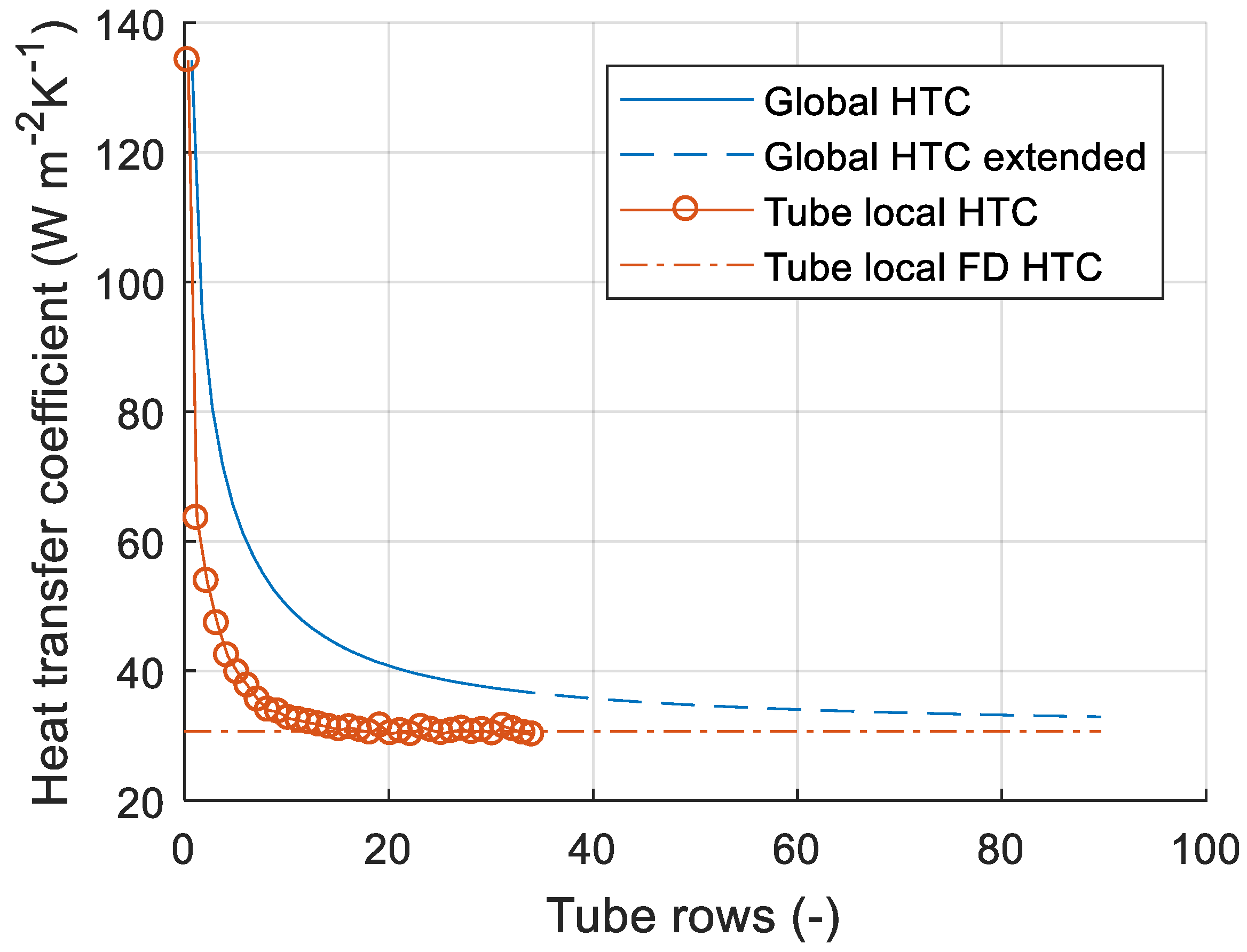
Overall heat transfer calculator. The demand for ceramic substrates with high mechanical strength and. Recently ceramic substrates have been of great interest for use in light emitting diode led packaging materials because of their excellent heat transfer capability. The data points were correlated in dimensionless form to provide a universal correlation for the estimation of heat transfer coefficients of any ceramic sponge using pressure drop data.
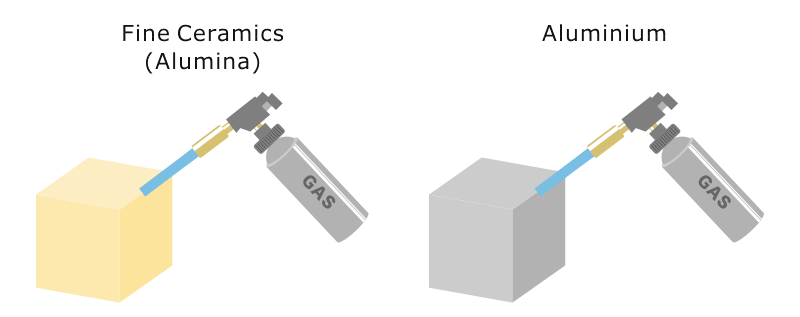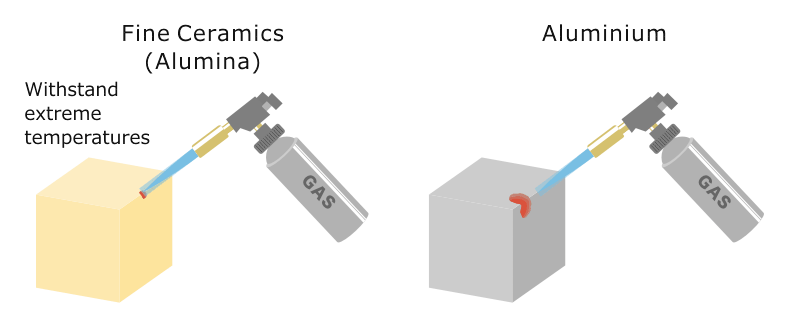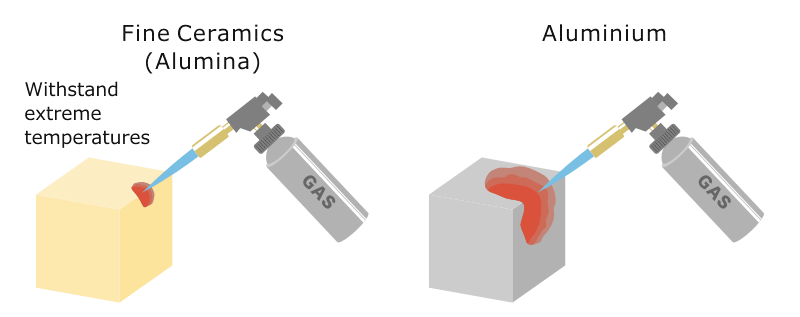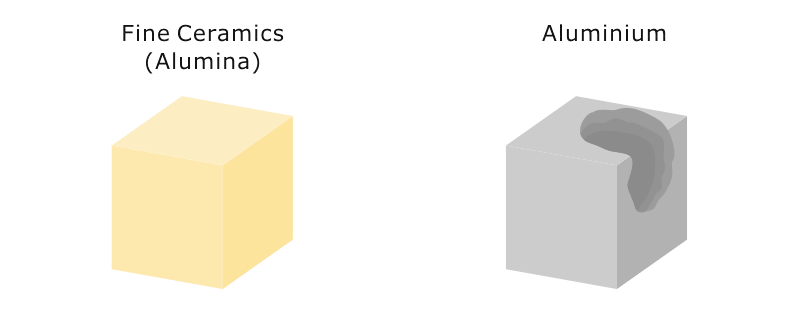
Conductive heat transfer through an aluminum pot wall with thickness 2 mm temperature difference 80 o c. H 0 is the heat transfer coefficient of the ceramic fiber cotton obtained from the cfd simulation w m 2 k 1 and h s is the heat transfer coefficient at the side of the specimen w m 2 k 1. Fine ceramics also known as advanced ceramics have low coefficients of thermal expansion less than half those of stainless steels. The coefficient ratio of thermal expansion indicates how much a material expands per 1 2 2 rise in temperature.
The radiant heat transfer coefficients on the inside and outside of the surfaces.
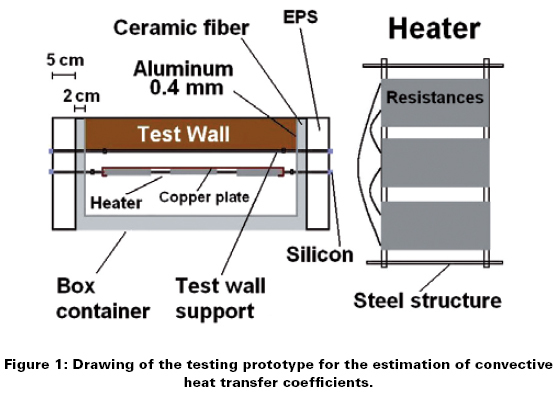


.jpg)