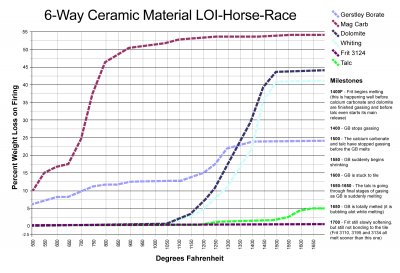
Ceramic Melting Graph

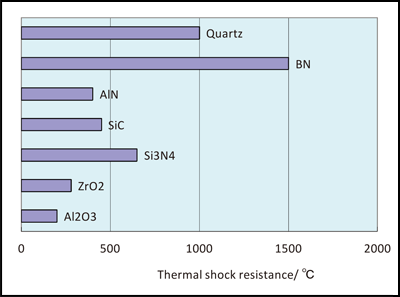
Broadly speaking uhtcs are borides carbides nitrides and oxides of early.
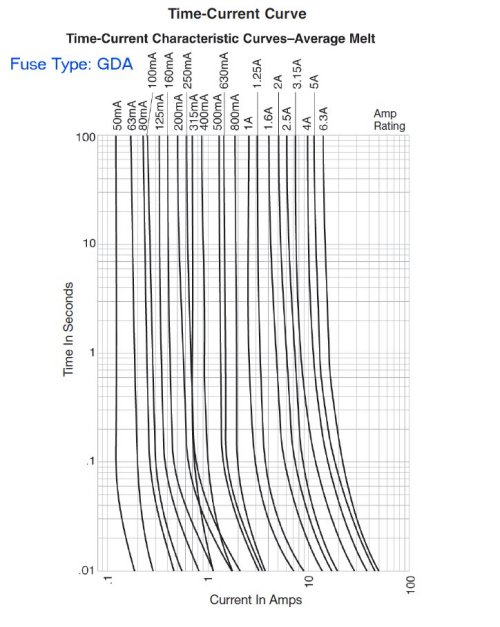
Ceramic melting graph. The key difference between glass and ceramic is that ceramics have crystalline or semi crystalline or non crystalline atomic structure whereas the atomic structure of glass is non crystalline. The maximum use temperature determines the temperature range in which a material is possible to use. Fuse s nominal melting i2t rating must also meet the inrush current requirements created by the input capacitor of the power supply s smoothing filter. Common ceramics include aluminum oxide melting point mp 3720 f titania 3245 f chrom.
Directionality of atomic bonding controls the structure and material properties viz melting temperature thermal ex pansion elastic stiffness electrical properties ductility and toughness etc. Ultra high temperature ceramics uhtcs are a class of refractory ceramics that offer excellent stability at temperatures exceeding 2000 c being investigated as possible thermal protection system tps materials coatings for materials subjected to high temperatures and bulk materials for heating elements. We use a vast range of ceramic materials in the day to day life. Materials with high melting point such as tungsten molybdenum and ceramics have various applications which require high heat resistance.
Melting glass in ceramics once upon a time when i was in high school my friend and i who had both decided to major in art education were given a lot of freedom to experiment in art class. Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications. Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics. As stated before they tend to have very high melting points compared to most metals.
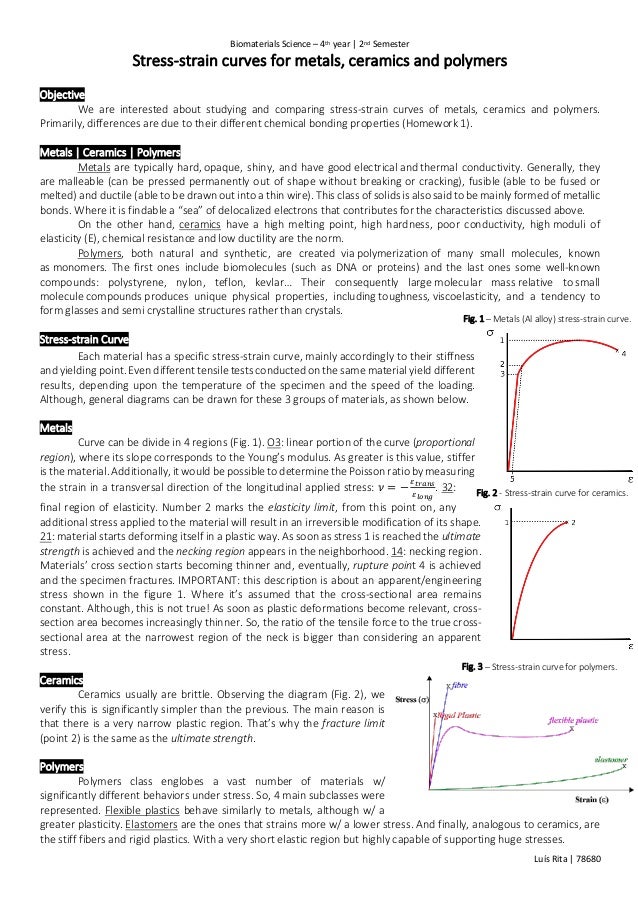
While some of the stress strain curves for polymers might look similar to ones for metals polymers are mechanically different than metals or ceramics. This paper attempts to bring out the correla tion between the potential energy curves with the properties of materials. Ceramics are refractory otherwise known as high melting point materials. Zirconium dioxide zro 2 sometimes known as zirconia not to be confused with zircon is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium its most naturally occurring form with a monoclinic crystalline structure is the mineral baddeleyite a dopant stabilized cubic structured zirconia cubic zirconia is synthesized in various colours for use as a gemstone and a diamond simulant.
For example furnance materials crucibles and heat shielding. Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids. The largest size fuse shown in the chart is the 5ag or midget. Ceramics and glass have many applications that require qualities such as hardness rigidity high resistance to heat corrosion etc.
Ceramic or a similar material other than glass.